Published
in Economy
Gold reserves of countries (2024) show the strategic importance of gold in national monetary systems. From the U.S. to France, the 2020–2024 period saw notable trends in central banks’ gold accumulation or stability.
Gold reserves refer to the quantity of gold held by a nation's central bank or monetary authority as part of its foreign exchange reserves. These reserves serve multiple purposes: stabilizing the currency, hedging against inflation, and strengthening investor confidence. Gold is considered a 'safe haven' asset, often increasing in value during economic uncertainty.
As of 2024, the United States leads with 8,133 tonnes of gold, a figure that has remained constant for decades. Germany follows with 3,352 tonnes, while Italy and France hold 2,452 and 2,437 tonnes respectively. These European nations have shown a trend of maintaining rather than expanding their gold stocks, viewing gold more as a legacy asset than an active monetary tool.
Between 2020 and 2024, most major economies preserved or marginally increased their gold holdings. China resumed gold purchases in late 2022, reaching 2,262 tonnes by 2024. India also steadily increased its reserves from approximately 687 tonnes in 2020 to 822 tonnes in 2024. In contrast, countries like the U.S., Germany, and France did not alter their reserves significantly, emphasizing policy continuity and reserve security.
Over 100 other countries hold less than 1% of global gold reserves each, totaling less than 4,000 tonnes combined. These include nations like Mexico, South Africa, and Turkey. Some, like Uzbekistan and Kazakhstan, actively increased reserves, while others liquidated portions. The diversity in strategies reflects local economic conditions and monetary policy goals.
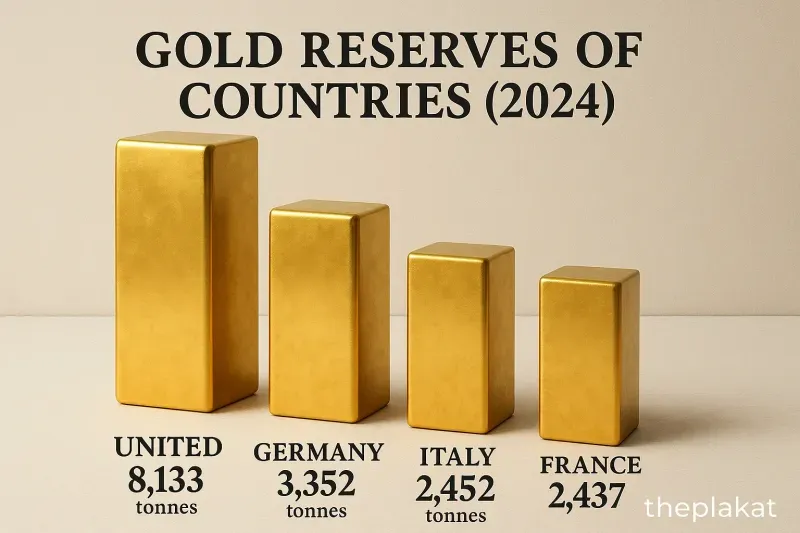
The United States holds the largest gold reserves in 2024, totaling 8,133 tonnes.
Yes, several countries including China and India increased their gold reserves, while major holders like the U.S. and Germany maintained their levels.
Central banks hold gold to stabilize national currencies, hedge against inflation, and build trust in the monetary system during times of economic instability.